Beginner TAP Tutorial - Single Table Usage in the Portal Aspect¶
This brief tutorial will show you how to perform the same data retrieval and analysis that is shown in the first of the Jupyter Notebook Tutorials (titled “Intro to DP0”) by using the Portal Aspect’s Single Table TAP search function.
In this tutorial we will extract data from a small region of sky in the object table and build a Color-Magnitude Diagram.
We assume that you have read the basic intro to the Portal Aspect in Introduction to the RSP Portal Aspect.
Select Portal Aspect from RSP¶
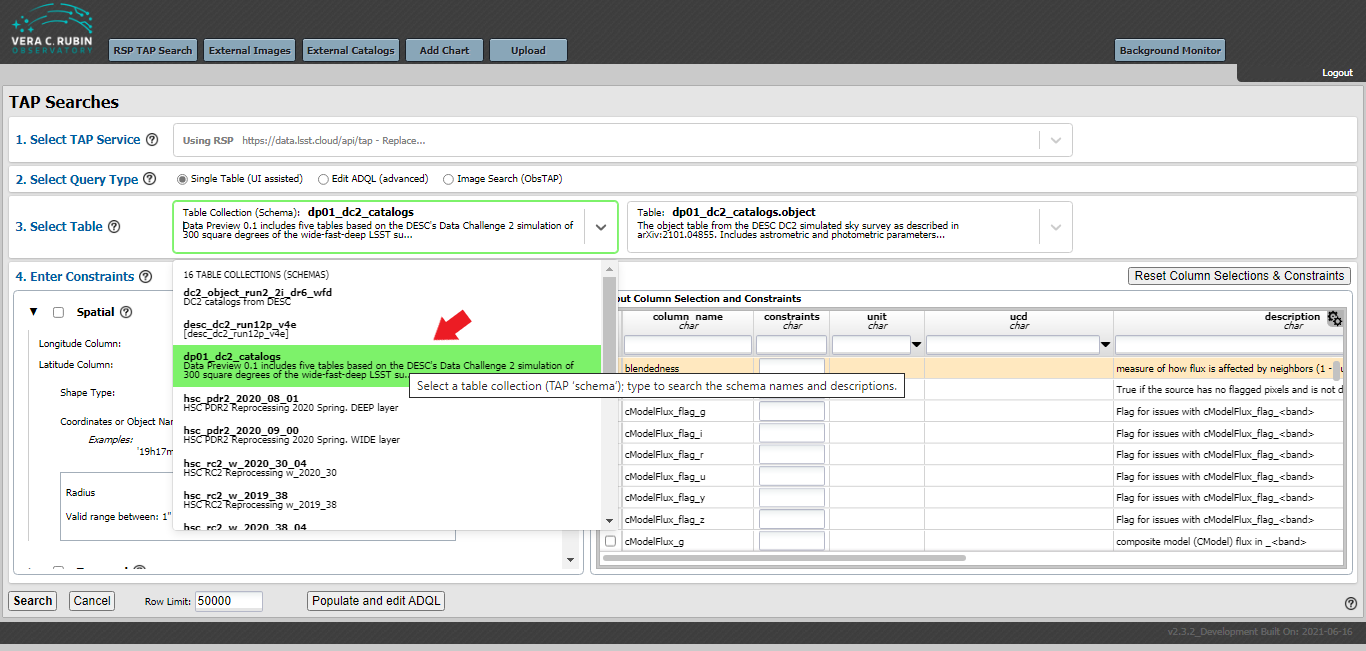
After logging into the Portal Aspect, select Single Table (UI assisted) from the Select Query Type, then select the dp01_dc2_catalogs (left) and dp01_dc2_catalogs.object (right) from the Select Table drop down menu.
(See figure below.)
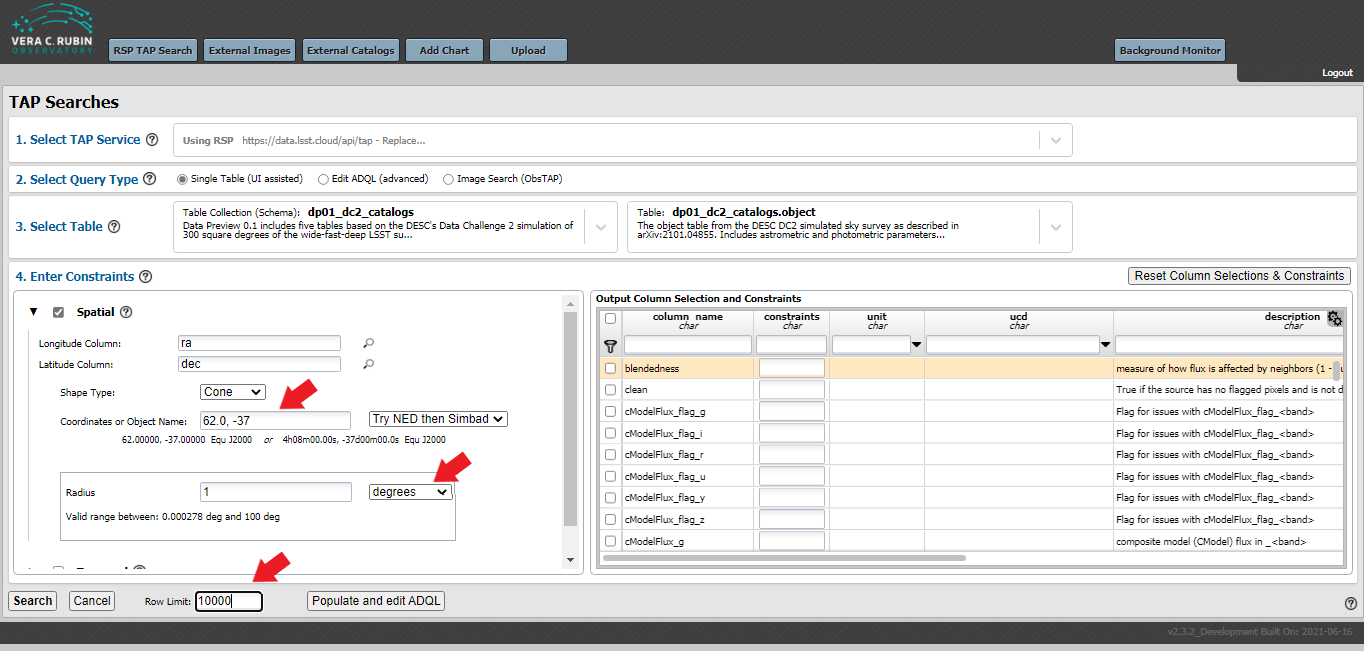
Next select the Spatial check box, the “Longitude Column” and “Latitude Column” should automatically populate with “ra” and “dec”. Enter the coordinates of 62.0, -37.0 in the “Coordinates or Object Name:” area. Choose a radius of 1 degree and select a row limit of 10,000 as shown in the photo below.
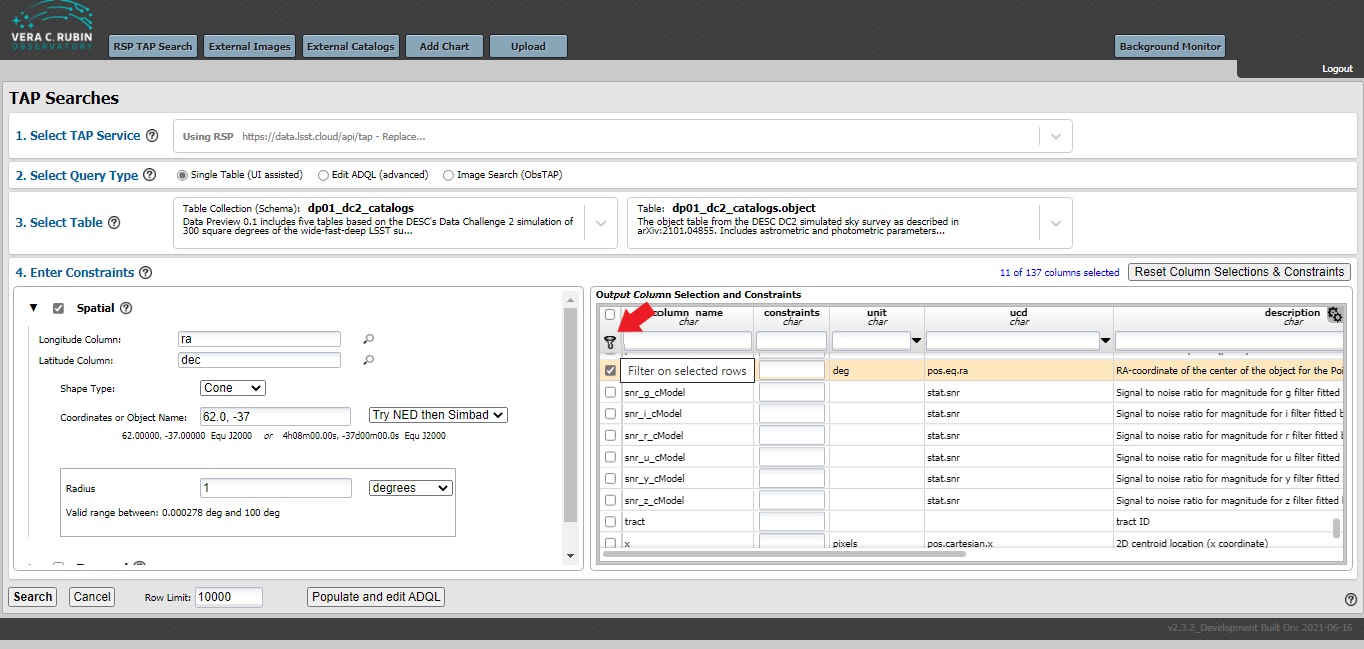
Select Columns for Analysis¶
In the Output Column Selection and Constraints window on the lower right hand side of the screen, select the following items: clean, dec, extendedness, good, mag_g, mag_i, mag_r, magerr_g, magerr_i, magerr_r, and ra. Use the search box under “column_name” to quickly find columns of interest: for example, type “mag” into that box and press enter to see only column names that contain “mag”. (See figure below.)
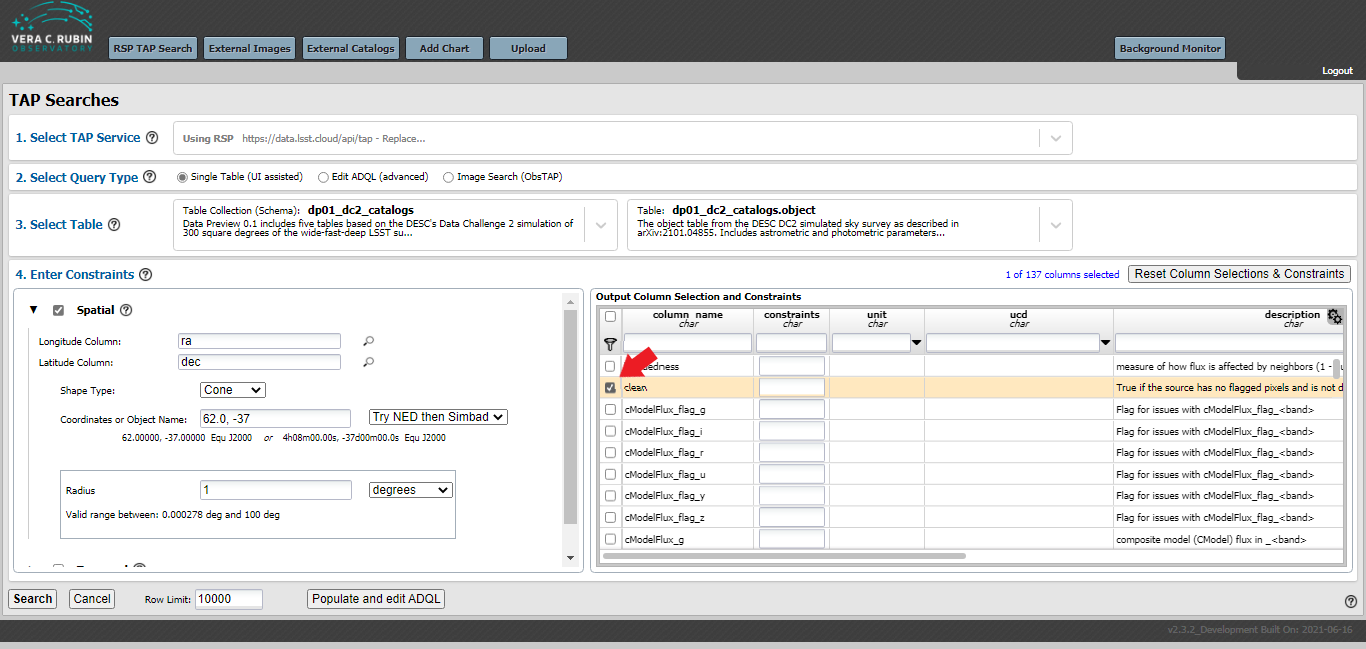
Then press the filter icon to select only those items for analysis.
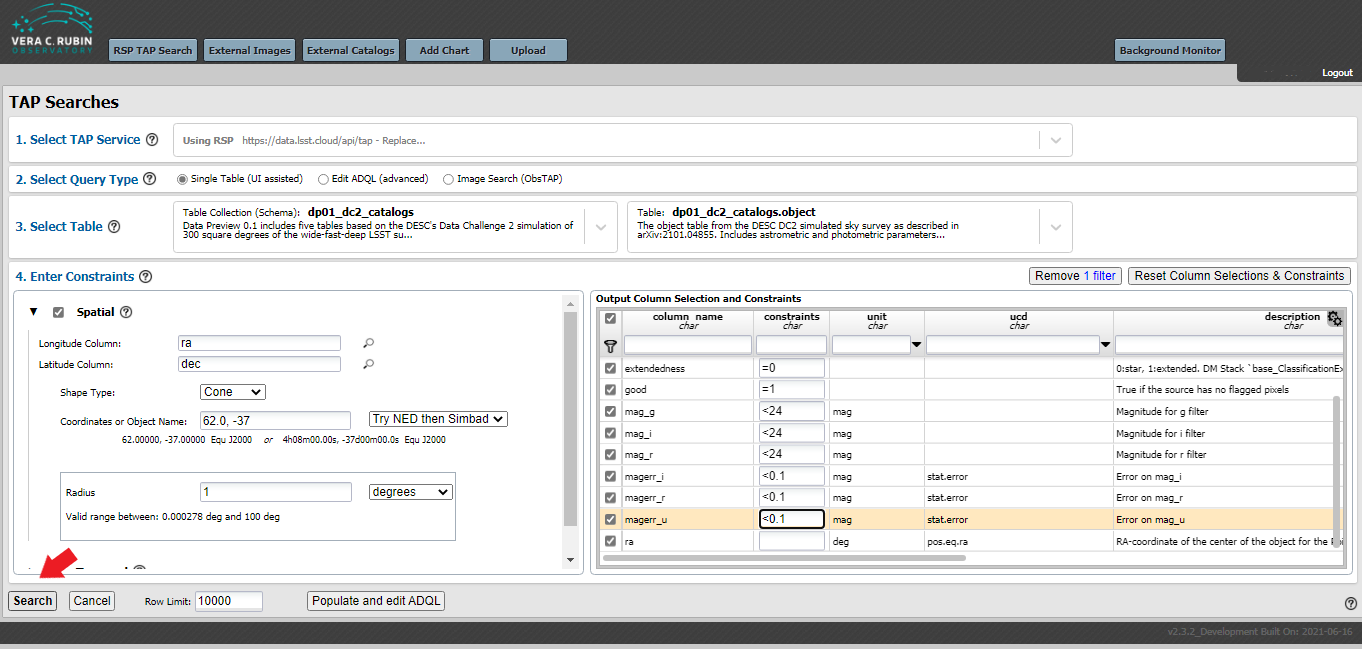
Select Columns Constraints¶
After you press the filter button you should have only those items you selected shown in the table. You may now add your column constaints to the table. For this example, use the following values: clean = 1, dec (leave blank), extendedness = 0, good = 1, mag_g <24, mag_i <24, mag_r <24, magerr_g < 0.1, magerr_i < 0.1, magerr_r < 0.1, ra (leave blank).
Then press the Search button as shown in the figure below.
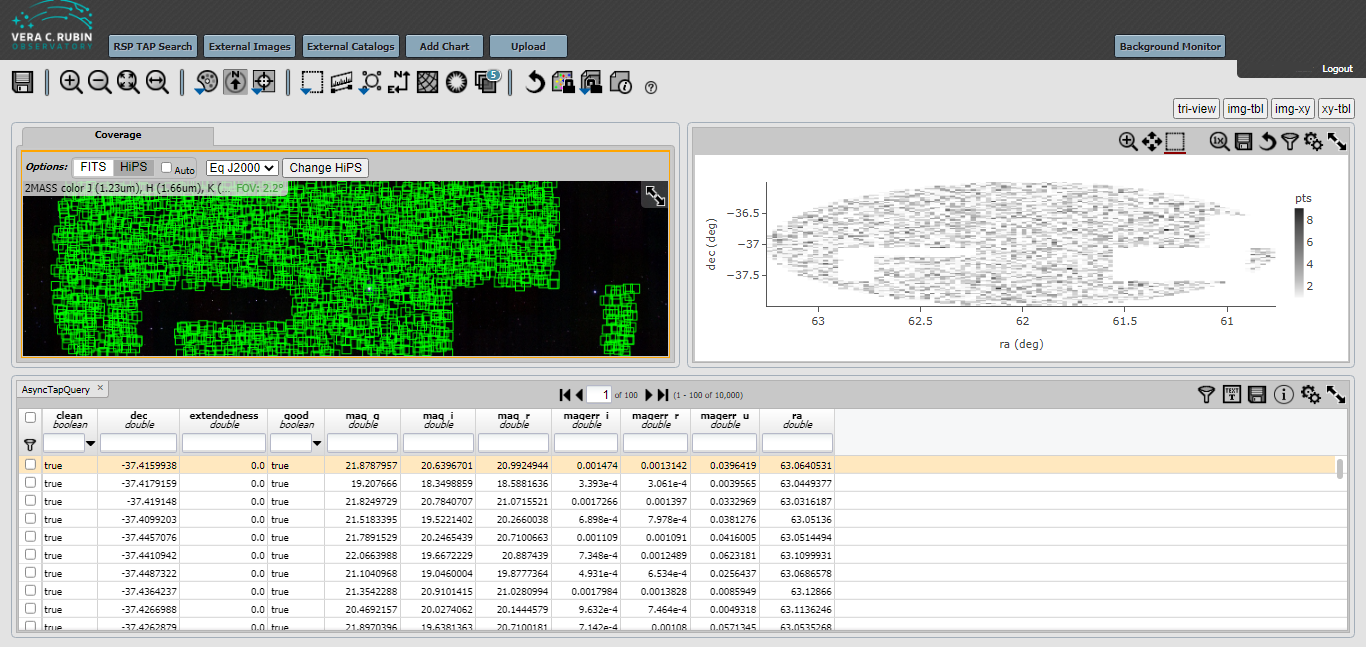
Select Configure the Graph to Create a Color Magnitude Diagram¶
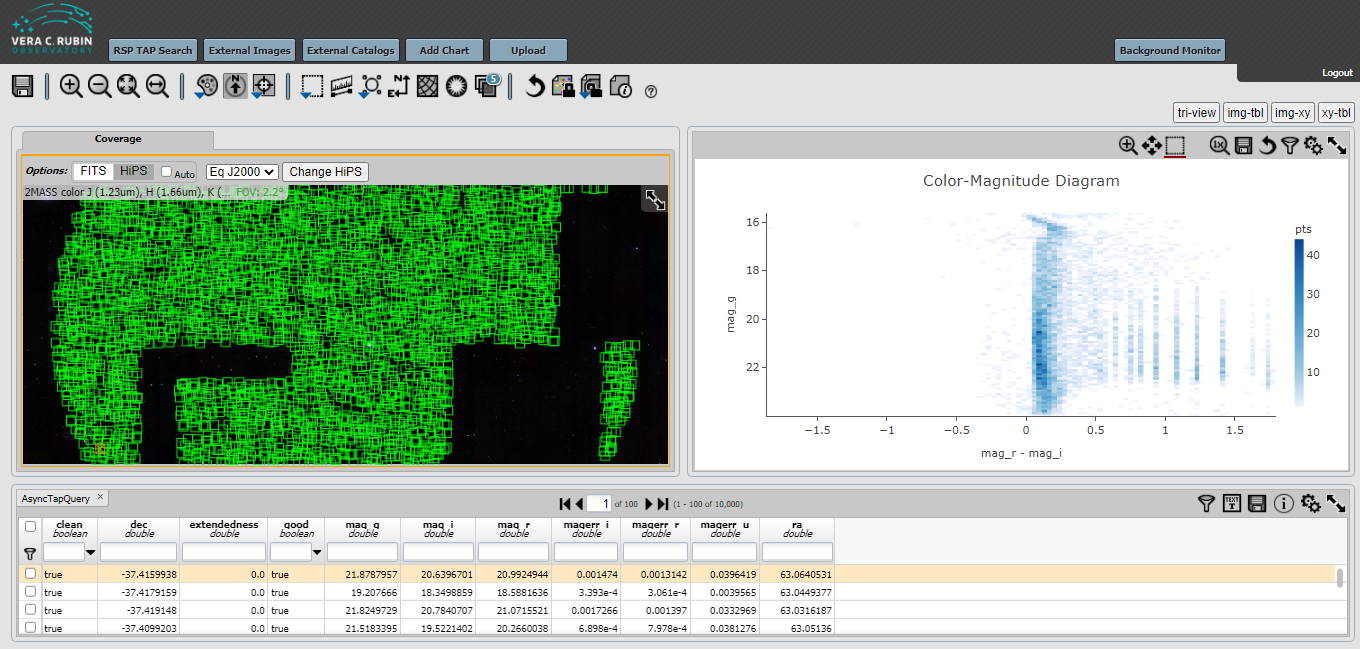
This figure shows the results of the search. The gaps in the spatial coverage of the returned catalog objects is due to the limit of 10000. The gaps for your search might be different from what is shown below.
Next, click on the double gear icon on the upper right hand window.
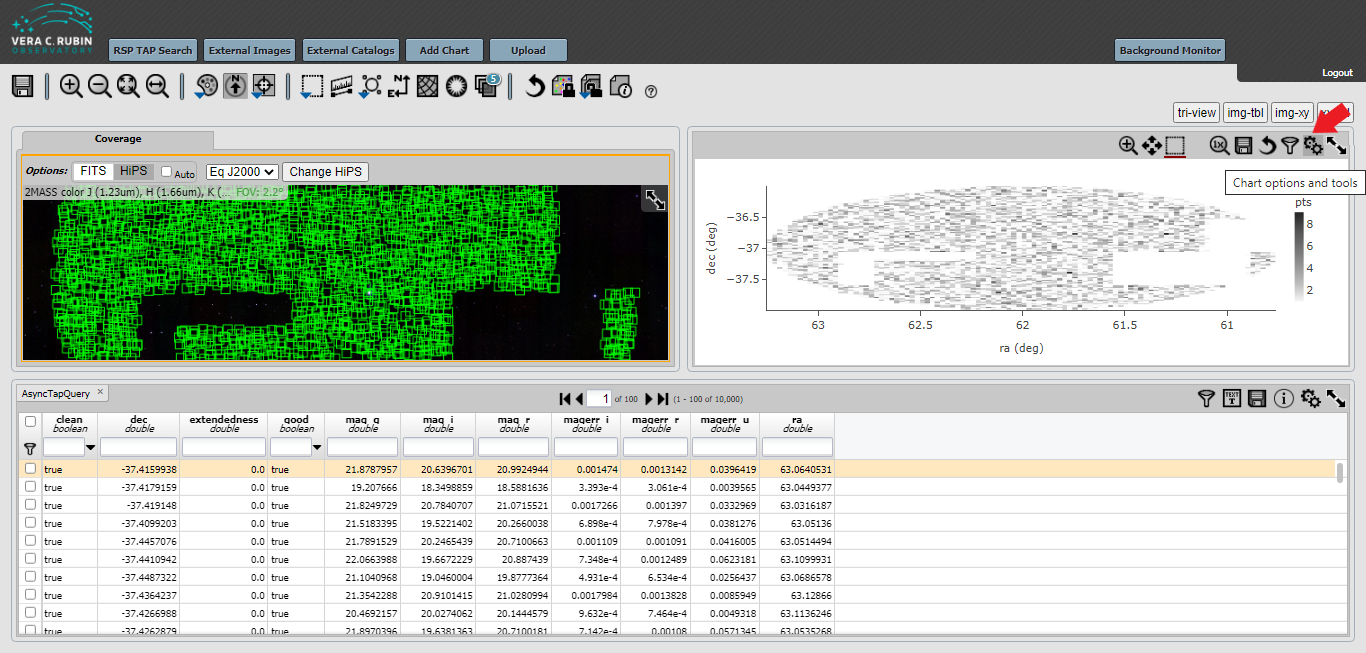
Finally, change the parameters in the selection box. The X should be “mag_r - mag_i” and the Y should be “mag_g”. Click on Chart Options and select reverse under the Y-Label.
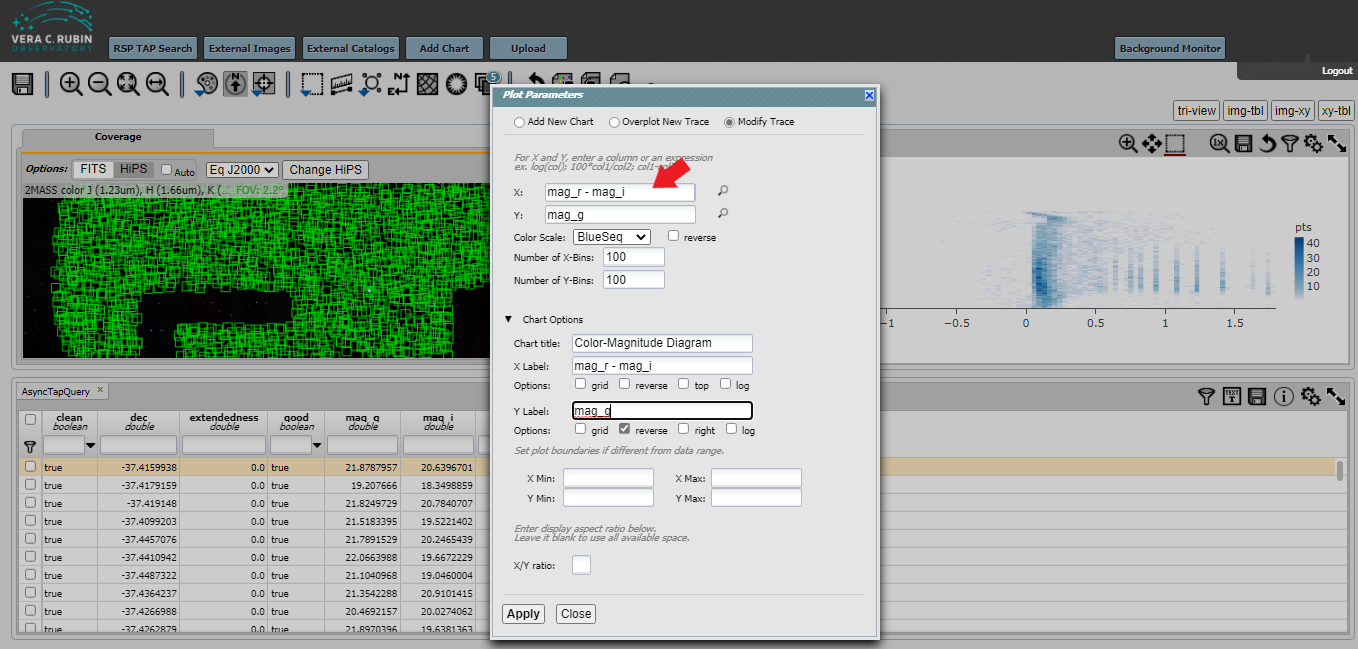
Then hit Apply. The plot that you make will be slightly different from what is shown below, and different from the plot in the first of the Jupyter Notebook Tutorials due to random sampling and the 10000 maximum that we used.